dEEpEst
☣☣ In The Depths ☣☣
Staff member
Administrator
Super Moderator
Hacker
Specter
Crawler
Shadow
- Joined
- Mar 29, 2018
- Messages
- 13,859
- Solutions
- 4
- Reputation
- 27
- Reaction score
- 45,545
- Points
- 1,813
- Credits
- 55,080
7 Years of Service
56%
We’re excited to announce that Hack Tools Dark [HTDark.CoM] is now accessible as a hidden service on the Tor network. This means you can enjoy enhanced privacy and anonymity while browsing our site.
To access our Tor version, simply use the
This link is hidden for visitors. Please Log in or register now.
This link is hidden for visitors. Please Log in or register now.
Why use Tor?
The Tor network is perfect for those who want to protect their privacy and avoid online censorship. By offering this option, we aim to provide our community with a safer and more secure way to access our content.What is the Tor Network?
The Tor Network (The Onion Router) is an online anonymity tool that allows users to browse the internet without revealing their location or identity. It works by routing internet traffic through a series of distributed nodes, hiding the user's real IP address and protecting their online activities. Tor was designed to safeguard users' privacy from surveillance or censorship.
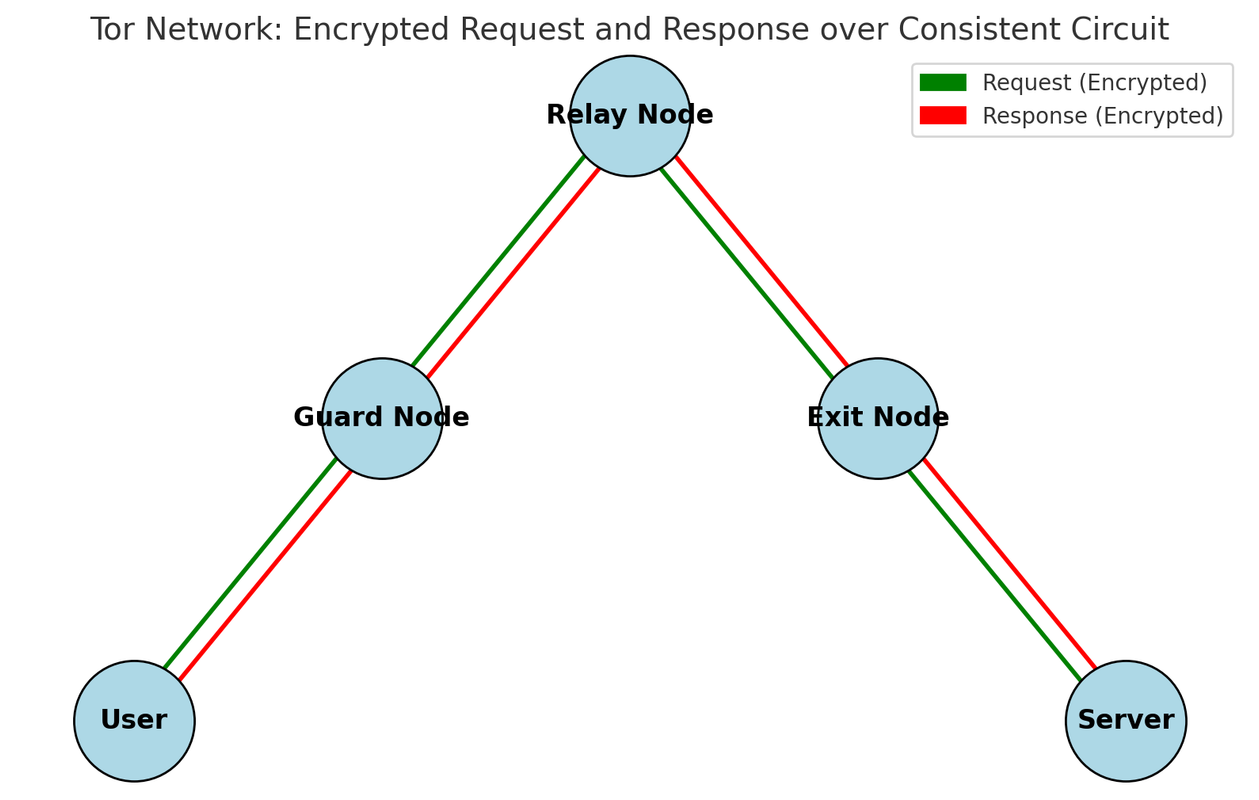
How Tor Works:
1. User's Request:
A user wants to visit a website or access a service online. Instead of connecting directly to the server, their request is encrypted multiple times and passed through several Tor nodes.2. Node Types:
Guard Node: This is the first node in the chain. It knows the user's real IP address but does not know the final destination.Relay Node: This is one of the intermediate nodes. It only knows which node passed it the data and which node it will pass the data to. It does not know the user's IP or the final destination.
Exit Node: This is the last node before reaching the final server. The server sees the IP address of this node, not the user's real IP.
3. Multi-layer Encryption:
Before the data is sent, it is encrypted in several layers. Each layer corresponds to one node. The Guard Node decrypts the outermost layer, revealing where to pass the request next. This process continues until the Exit Node removes the final layer and sends the request to the server.4. Response:
The server sends the response back to the Exit Node, and the response travels backward through the nodes in the same manner, with each node encrypting the data again, until it reaches the user.Encryption:
Tor uses multi-layer encryption, where each layer is peeled away by a different node. This ensures that no single node knows the entire path of the communication, making it difficult to trace the user's activities.Benefits of Tor:
Privacy:
The user's identity is hidden as the server only sees the Exit Node's IP address.Anonymity:
Since the traffic is split across multiple nodes, it's hard for any one entity to trace the full communication path.Circumventing Censorship:
Tor is commonly used to bypass internet censorship in restrictive regions.If you have any questions or need help connecting to our Tor site, feel free to reach out. Thank you for your continued support!
Last edited: